

Increased dipolarity increases the less electronegative (positively charged) atom to be more susceptible to nucleophilic attack.Effect is relatively weak and gets increasingly weaker as you move farther away from the more electronegative atom.Differing electronegativity’s between two molecules of a sigma bond cause one end to be positive and the other to be slightly negative.Induction: the distribution of charge across sigma bonds.In general, the size and substitution of the leaving group affects the ability of the nucleophile to access the carbonyl carbon.Also can be positive since it can help force a certain type of reaction or help in the generation of protecting groups.Can be seen as a detrimental effect since reactivity is decreased.Steric hindrance is when a reaction does not proceed due to the size of its substituents.Amides have an electron donating amine group and are thus the least reactive.Esters are second most reactive since they contain one less oxygen atom.Anhydrides are most reactive since their resonance stability and three electron withdrawing oxygen atoms are the most electrophilic and thus reactive.Reactivity of the carbonyl is determined by the substituents.
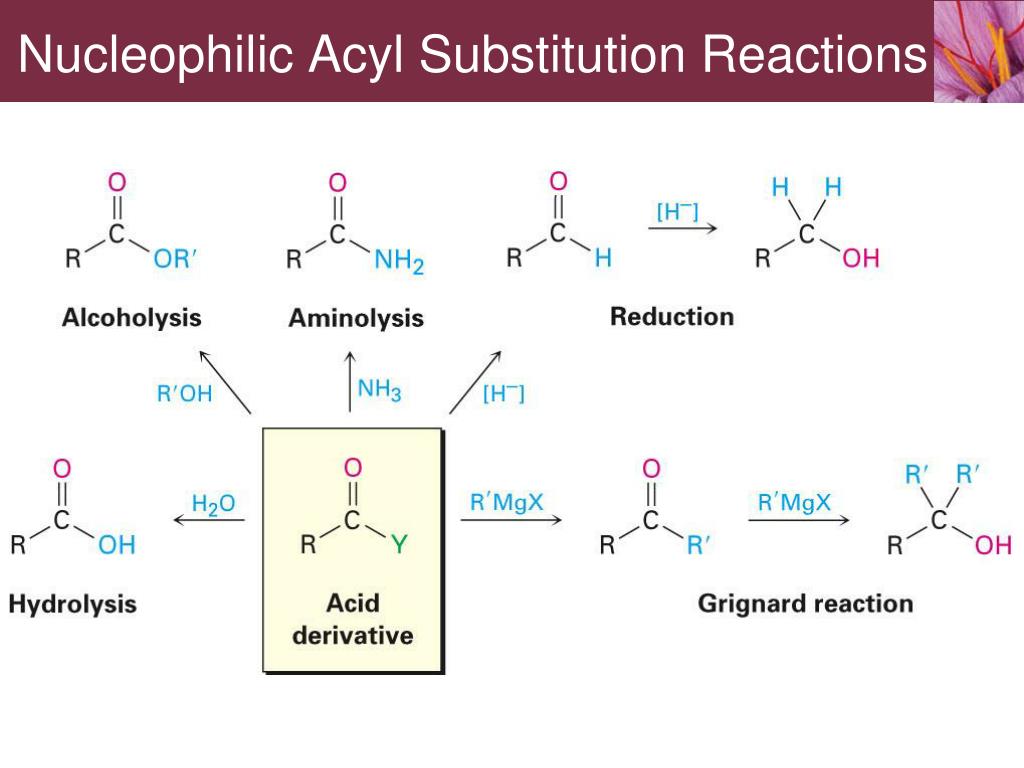
Have higher boiling points than corresponding carboxylic acids since they are much heavier.Only anhydrides with five or six membered rings are made easily.Reaction is driven forward by the increased stability of the newly formed rings.Cyclic anhydrides can be formed by heating the carboxylic acids.Hydroxyl group of one acts as a nucleophile and attach the carbonyl group on the other.Synthesized by the condensation reaction between two carboxylic acids and one molecule of water is lost in condensation.If asymmetrical, name two chains alphabetically and then followed by anhydride.Symmetrical anhydrides are named by substituting anhydride for acid in a carboxylic acid.Also called Acid anhydrides and are the condensation dimers of carboxylic acids which have the general formula RC(O)OC(O)R.Can undergo Saponification to produce soap salts.Esters of long chain carboxylic acids and glycerol.Triacylglycerol: storage forms of fats in the body.Lack hydrogen bonding, so boiling points are lower than related carboxylic acids.Lactones: Cyclic esters and named similarly to lactones, but with name of precursor acid molecule included.Fischer Esterification: mixing carboxylic acids and alcohols under acidic conditions so that they condense into esters.Named by placing the esterifying group as a prefix and the –oate suffix replaces -oic acid.Esterification Group: substituent that is bonded to the oxygen.Dehydration synthesis products of other carboxylic acid derivatives and alcohols.May or may not participate in hydrogen bonding.Lactams: Cyclic amides and are named according to the carbon atom that is bonded to the nitrogen.



 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
